Skip to main contentCybersecurity threats are malicious activities that attempt to damage, steal, or disrupt digital assets. As technology advances, cyber threats become more sophisticated, making security awareness and preventive measures crucial for individuals and organizations.
Categories of Security Threats
Security threats can be classified into various categories:
- Malware - Malicious software that infects systems.
- Phishing - Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive data.
- Social Engineering - Manipulating people into revealing confidential information.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks - Overloading systems to cause downtime.
- Ransomware - Encrypting files and demanding ransom for access.
- Data Breaches - Unauthorized access to confidential data.
- Insider Threats - Security risks from within an organization.
- Zero-Day Exploits - Attacks that target undisclosed software vulnerabilities.
1. Malware
What is Malware?
Malware (malicious software) is designed to infiltrate and damage systems. Types of malware include:
- Viruses: Attach to files and spread when executed.
- Worms: Self-replicate and spread through networks.
- Trojan Horses: Disguised as legitimate software.
- Spyware: Secretly collects user information.
- Adware: Displays unwanted advertisements.
Diagram: Malware Infection Process
How to Prevent Malware
- Install and update antivirus software.
- Avoid downloading files from unknown sources.
- Use a firewall to monitor network traffic.
2. Phishing
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a cyber-attack that tricks users into providing personal information by pretending to be a legitimate entity.
Common Phishing Techniques
- Email Phishing: Fraudulent emails requesting sensitive data.
- Spear Phishing: Targeted attacks on individuals or organizations.
- Smishing: Phishing through SMS messages.
- Vishing: Voice phishing over phone calls.
Image: Example of a Phishing Email
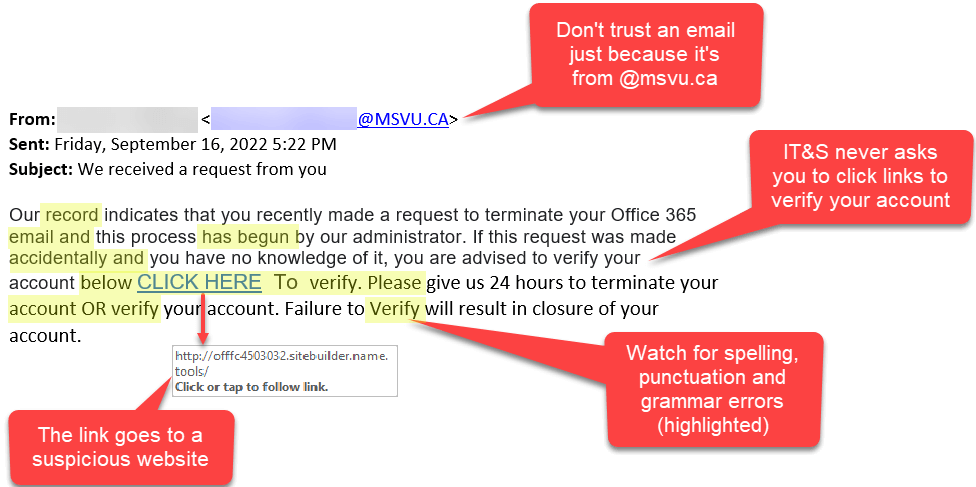
How to Prevent Phishing
- Do not click on suspicious links.
- Verify sender details before responding.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA).
3. Social Engineering
What is Social Engineering?
Social engineering exploits human psychology to manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information.
Types of Social Engineering Attacks
- Pretexting: Creating a fabricated scenario to obtain data.
- Baiting: Offering free software infected with malware.
- Tailgating: Gaining unauthorized access by following an authorized user.
How to Prevent Social Engineering
- Train employees on security awareness.
- Verify identities before sharing sensitive data.
- Avoid oversharing personal information online.
4. Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks
What are DoS and DDoS Attacks?
A Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack floods a target system with excessive requests, making it unavailable.
A Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack uses multiple compromised devices (botnets) to amplify the attack.
Diagram: DDoS Attack Flow
How to Prevent DoS and DDoS Attacks
- Use anti-DDoS solutions and firewalls.
- Monitor network traffic for anomalies.
- Implement rate limiting and content delivery networks (CDNs).
5. Ransomware
What is Ransomware?
Ransomware encrypts user files and demands a ransom payment to restore access.
Ransomware Attack Process
- User downloads a malicious file.
- Ransomware encrypts critical files.
- Attacker demands a ransom payment.
- Victim either pays or loses data permanently.
How to Prevent Ransomware
- Regularly back up data.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links or attachments.
- Keep software and security patches up to date.
6. Data Breaches
What is a Data Breach?
A data breach occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive information.
Causes of Data Breaches
- Weak passwords.
- Unpatched software vulnerabilities.
- Insider threats and misconfigured security settings.
How to Prevent Data Breaches
- Encrypt sensitive data.
- Use strong passwords and MFA.
- Conduct regular security audits.
7. Insider Threats
What are Insider Threats?
Insider threats originate from employees, contractors, or business associates who misuse their access to harm the organization.
How to Mitigate Insider Threats
- Limit access based on job roles.
- Monitor employee activities.
- Establish strict data policies.
8. Zero-Day Exploits
What are Zero-Day Exploits?
Zero-day exploits target vulnerabilities that are unknown to software vendors, making them highly dangerous.
How to Prevent Zero-Day Attacks
- Regularly update software.
- Use intrusion detection systems.
- Employ threat intelligence services.
Conclusion
Understanding common security threats is crucial for building a secure digital environment. Implementing best practices such as strong authentication, security awareness training, and continuous monitoring can significantly reduce risks and protect sensitive information from cyber-attacks.
Stay informed, stay secure! 

