Introduction
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured process used in software development to ensure high-quality software is developed in a cost-effective and timely manner. It consists of multiple phases that guide the development process from planning to deployment and maintenance.Phases of SDLC
- Requirement Analysis – Understanding project needs and gathering user requirements.
- Planning – Defining scope, resources, costs, and timelines.
- Design – Creating architecture and system design.
- Implementation (Coding) – Writing and compiling code based on design specifications.
- Testing – Verifying functionality, security, and performance.
- Deployment – Releasing the software for user access.
- Maintenance – Providing updates, fixing bugs, and improving performance.
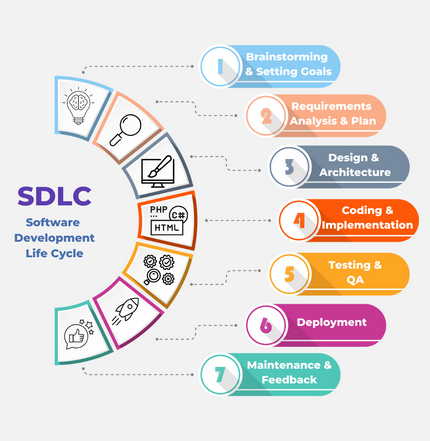
SDLC Models
Different SDLC models define how these phases are carried out. Let’s explore them in detail.1. Waterfall Model
About:
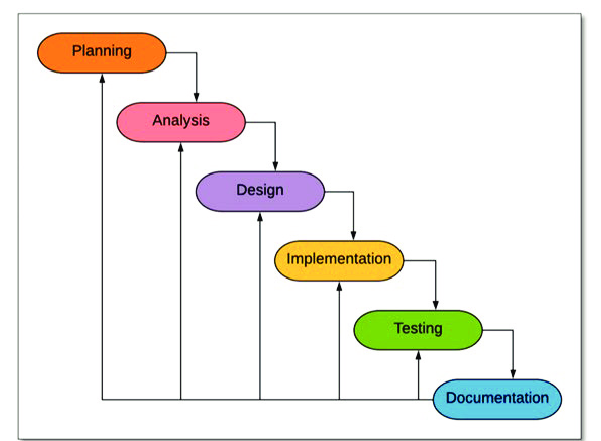
The Waterfall Model is a linear and sequential approach where each phase is completed before moving to the next.How It Works:
- Requirements are gathered at the beginning.
- Phases progress in a step-by-step manner.
- Changes are difficult to accommodate once the process has started.
Pros:
✅ Simple and easy to understand. ✅ Works well for projects with clear requirements. ✅ Each phase has specific deliverables.Cons:
❌ Not flexible for changes. ❌ High risk of failure if requirements are incorrect. ❌ Testing happens late, which can be costly.2. Agile Model
About:
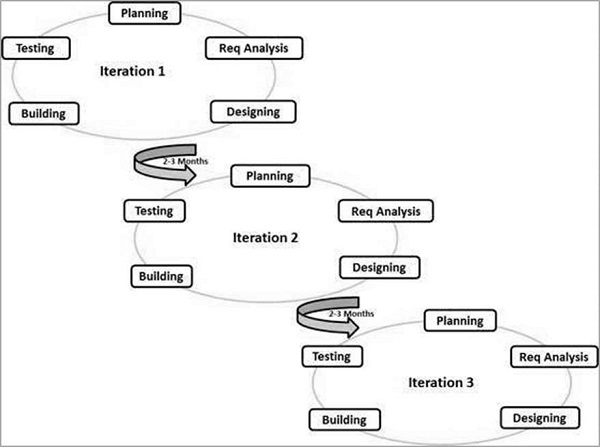
Agile is an iterative and flexible approach that delivers software in small, incremental cycles.How It Works:
- Development is divided into short sprints (typically 2-4 weeks).
- Regular feedback is taken from customers.
- Continuous testing and improvement occur throughout development.
Pros:
✅ Highly flexible and adaptable. ✅ Frequent deliveries improve customer satisfaction. ✅ Continuous testing ensures quality.Cons:
❌ Requires constant communication. ❌ Not suitable for small teams or projects with fixed budgets. ❌ Frequent changes can lead to scope creep.3. Spiral Model
About:
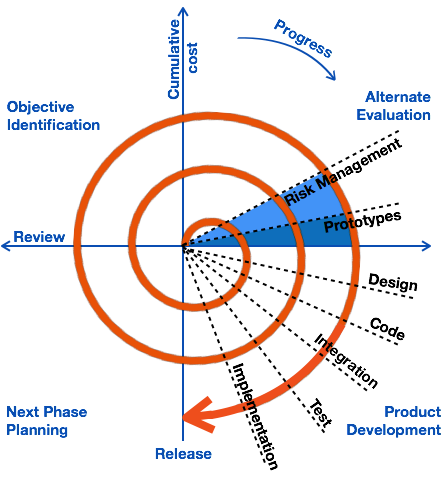
The Spiral Model combines iterative development with risk assessment.How It Works:
- Each iteration follows four phases: planning, risk analysis, development, and evaluation.
- Risks are identified and mitigated early.
- Used for large, complex projects with evolving requirements.
Pros:
✅ Risk management is a priority. ✅ Suitable for large-scale projects. ✅ Flexible and iterative.Cons:
❌ Expensive due to risk management efforts. ❌ Complex and time-consuming. ❌ Requires experienced developers.4. Iterative Model
About:
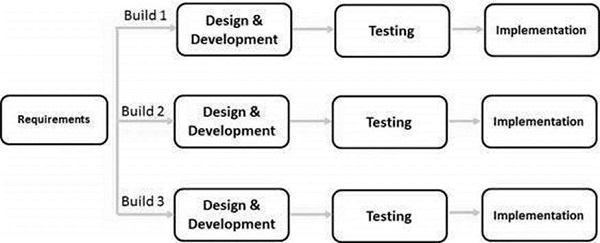
The Iterative Model develops software in repeated cycles, refining it over time.How It Works:
- A basic version is built quickly and improved iteratively.
- Each cycle adds new features and fixes problems.
- Used when requirements are unclear at the start.
Pros:
✅ Allows feedback-driven improvements. ✅ Early software versions available. ✅ Suitable for changing requirements.Cons:
❌ More resource-intensive than linear models. ❌ Requires strong planning. ❌ Design flaws may persist if not corrected early.5. V-Model (Validation and Verification)
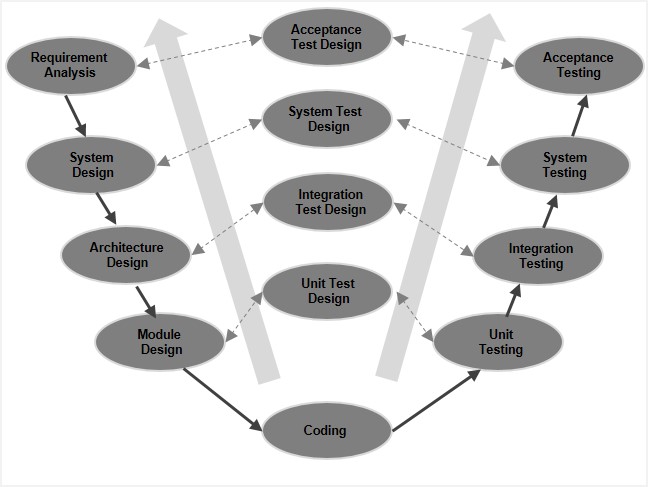
About:
The V-Model is an extension of the Waterfall Model where each development phase has a corresponding testing phase.How It Works:
- Each phase has a corresponding validation stage.
- Testing is emphasized early in the process.
- Useful for safety-critical systems like medical and aviation software.