Skip to main contentIntroduction
In the digital age, passwords are the first line of defense against unauthorized access to sensitive information. Weak passwords can lead to identity theft, financial loss, and data breaches. Understanding password security and implementing best practices can significantly reduce cyber risks.
Why Password Security is Important
- Protects Personal & Financial Data: Prevents unauthorized access to banking, social media, and personal accounts.
- Prevents Identity Theft: Hackers use weak passwords to impersonate individuals.
- Secures Corporate & Government Systems: Weak passwords can lead to large-scale data breaches.
Common Password Attacks
Cybercriminals use various techniques to compromise passwords. Here are the most common ones:
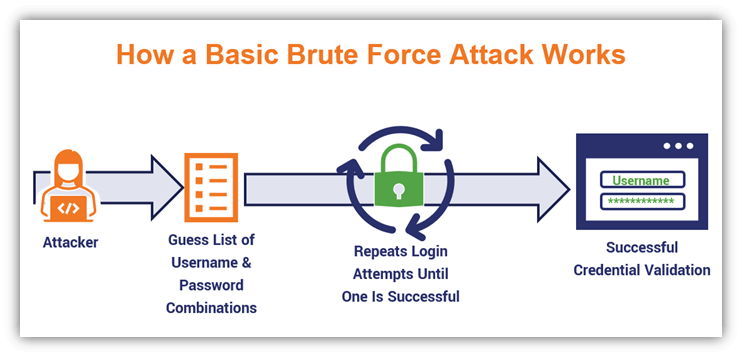
1. Brute Force Attack
A hacker systematically tries all possible password combinations until the correct one is found.
2. Dictionary Attack
Uses a predefined list of commonly used passwords and phrases to guess login credentials.
3. Phishing Attack
Tricks users into revealing their passwords through fake emails, websites, or messages.
4. Credential Stuffing
Hackers use previously leaked usernames and passwords to gain access to multiple accounts.
5. Keylogging
Malware records keystrokes to steal login credentials.
Best Practices for Strong Password Security
1. Use Strong and Unique Passwords
A strong password should:
- Be at least 12-16 characters long
- Include uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters
- Avoid common words, names, and birthdays
Example of a Strong Password
2. Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification, such as:
- One-time passwords (OTP) via SMS or email
- Authentication apps like Google Authenticator
- Biometrics (fingerprint, facial recognition)
3. Use a Password Manager
Password managers securely store and generate strong passwords, reducing the risk of weak or reused passwords.
4. Avoid Reusing Passwords
Using the same password across multiple accounts increases vulnerability if one is compromised.
5. Regularly Update Passwords
Change passwords every 3-6 months to minimize the risk of compromised credentials.
6. Monitor for Data Breaches
Use services like Have I Been Pwned to check if your credentials have been exposed in breaches.
Implementing Secure Authentication Systems
Organizations should adopt advanced authentication mechanisms, such as:
- Salted & Hashed Password Storage: Use cryptographic hashing algorithms like bcrypt, Argon2, or PBKDF2 to store passwords securely.
- Account Lockouts & CAPTCHA: Prevent automated brute-force attacks.
- Biometric Authentication: Use fingerprints or facial recognition for enhanced security.
Conclusion
Password security is a critical aspect of online safety. By following best practices, enabling multi-factor authentication, and using password managers, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce the risk of cyber threats. Stay vigilant and prioritize security in all online activities. 

